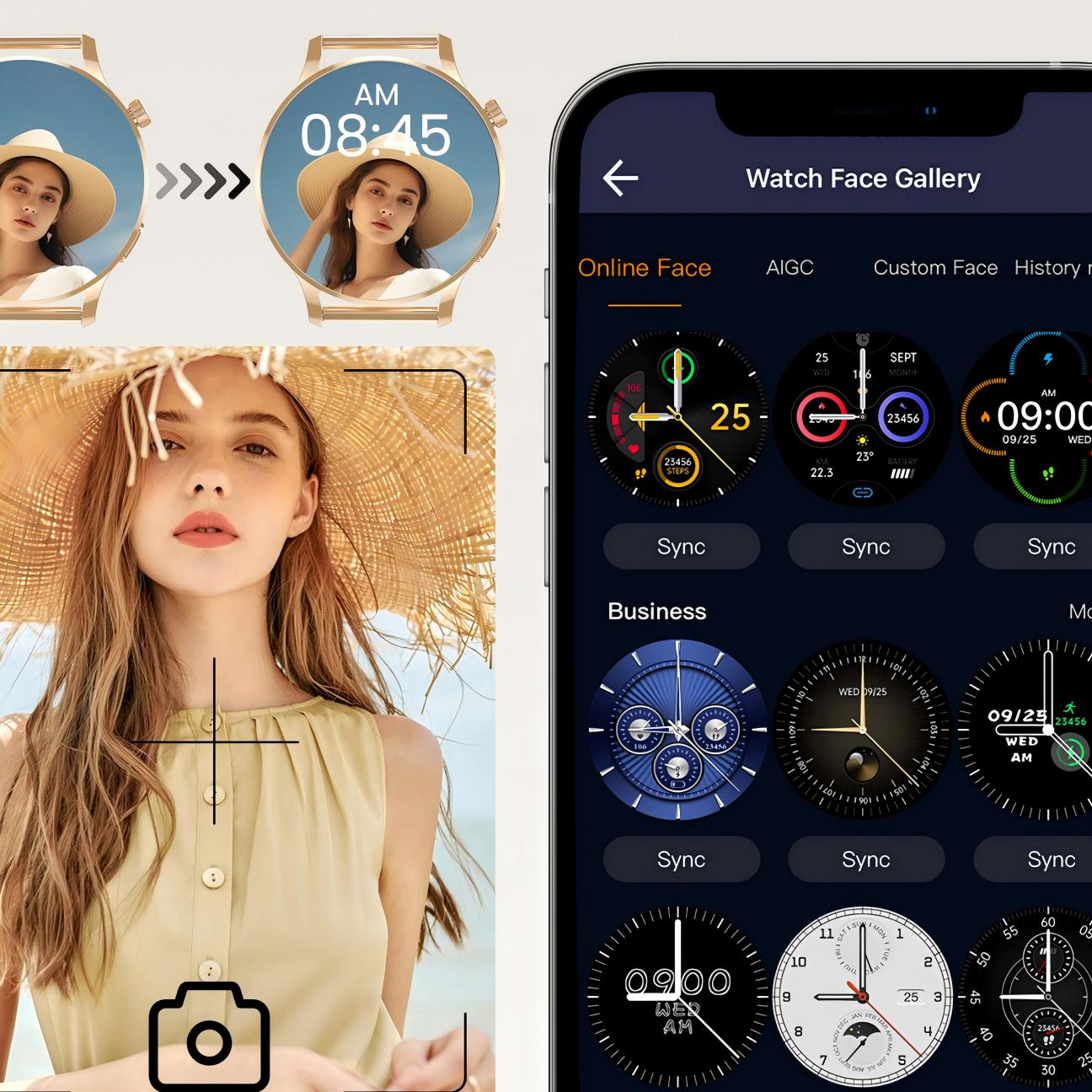
A Guide to Wearable ECG Smart Watches
Use electrocardiogram to track atrial fibrillation &protect heart health.
Electrocardiograms (ECGs) play a vital role in identifying Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) and tracking episodes over time. With the advent of smartwatches equipped with ECG functionality, individuals with AFib can now monitor their heart rhythm at home, anytime symptoms arise. This empowers users to capture important data on arrhythmias, enabling more informed discussions and effective treatment planning with their healthcare provider
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib or AF) is a common heart condition where the heart beats irregularly, sometimes too fast or too slow.
Why are ECGs Critical in detecting and managing AFib?
An ECG, or electrocardiogram, records the heart's electrical activity and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing and monitoring AFib, as well as a variety of other heart conditions. It is a painless and non-invasive test that measures the heart’s electrical signals.
A traditional ECG conducted in a clinical or hospital setting uses 12 electrodes placed on specific areas of the body to capture the heart's electrical activity from multiple angles. These electrodes, which are small adhesive patches applied to the skin, generate a recording displayed as a series of waves representing heart rhythm intervals. This recording is analyzed by a cardiologist. The 12-lead ECG is regarded as the gold standard for ECG testing and is most commonly used in clinical environments.
Cardiologists examine the waveforms’ shapes, their components, the frequency of occurrence, and the regularity or variability of intervals between them. Specialists in heart rhythms, known as cardiac electrophysiologists, use this detailed information to diagnose a wide range of cardiac conditions. The 12-lead ECG also allows these experts to pinpoint the exact location of any abnormalities within the heart.
Do smart wearable devices detect AFib?

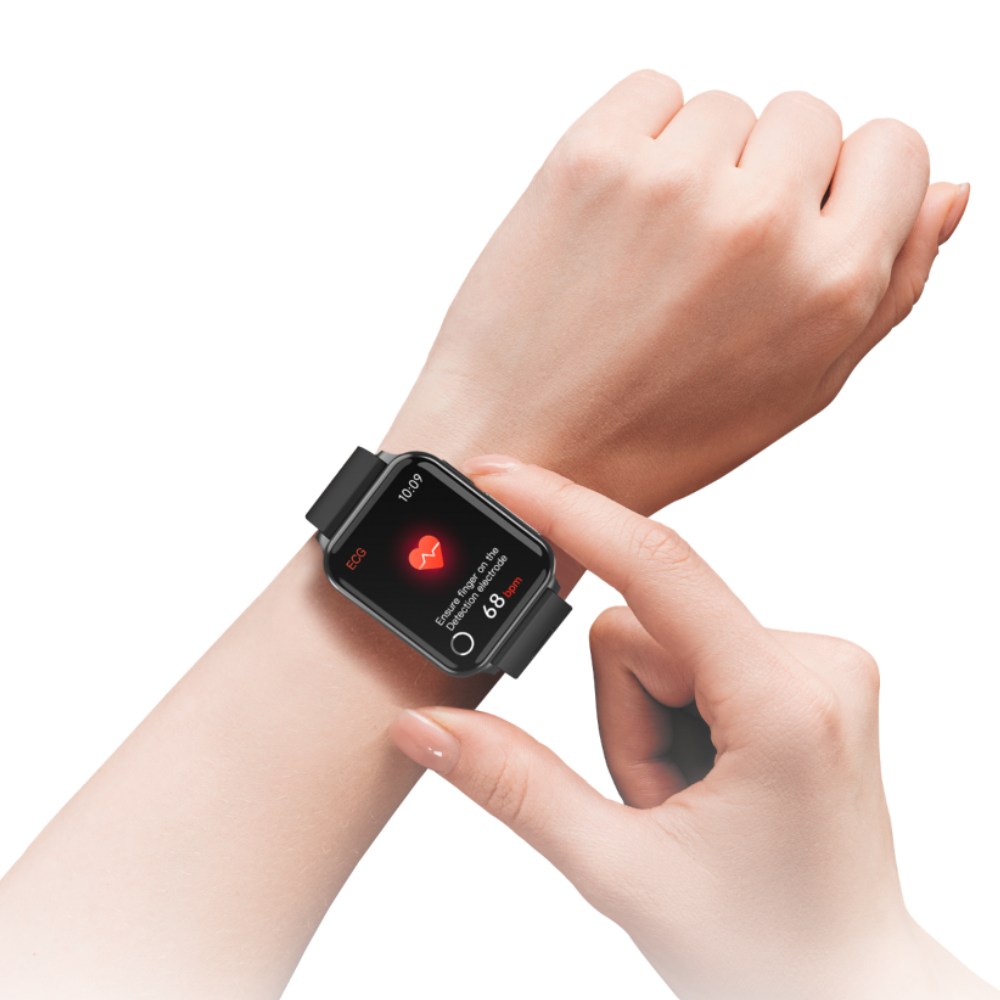
- The introduction of advanced wearable technology has made it possible for users to take an ECG directly from their wrist using a smartwatch. With built-in electrodes, these devices allow wearers to record their heart’s electrical activity and view the results instantly.
- Beyond recording ECGs, smartwatches leverage sophisticated algorithms to detect specific heart rhythm abnormalities, especially Atrial Fibrillation (AFib). Some devices can even notify users of potential signs of AFib, enabling many individuals to become aware of the condition through ecg smartwatch for the first time.
What sets wearable ECGs apart from 12-lead ECGs?
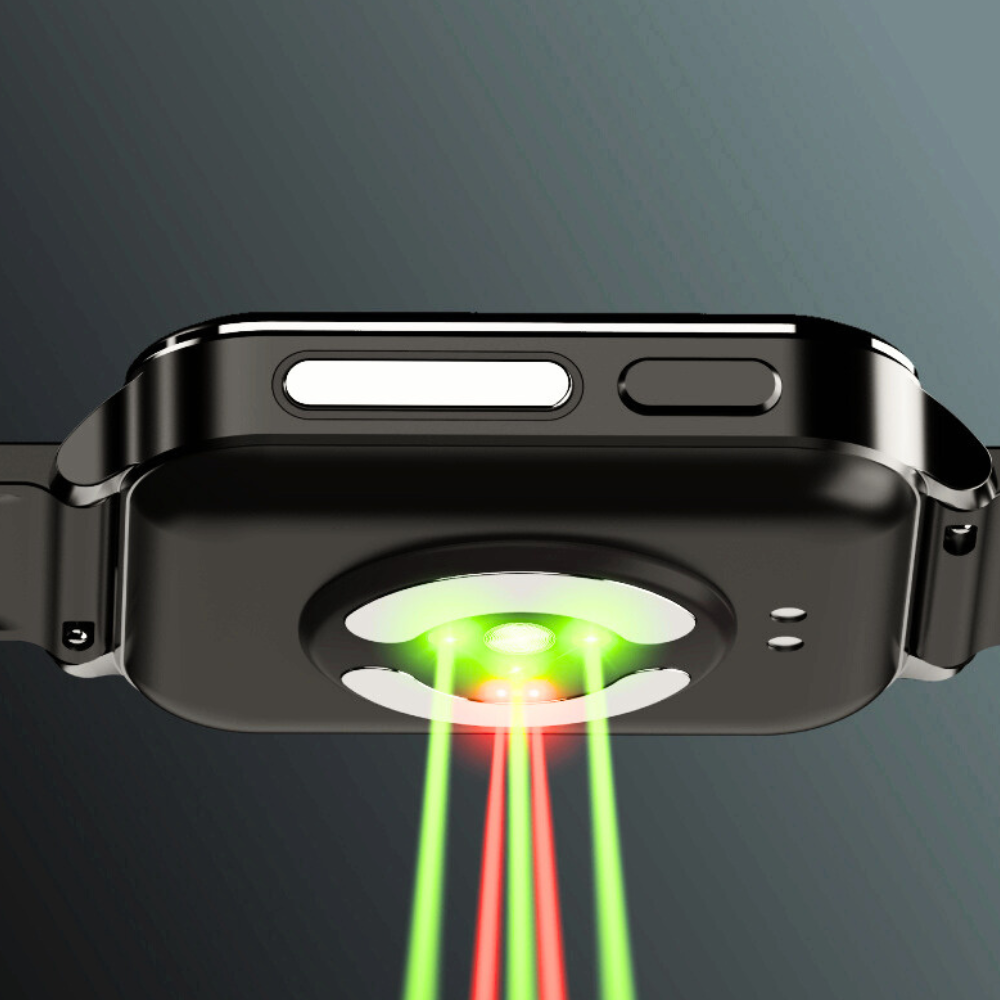
- Smartwatches or wearable ECGs utilize a single electrode sensor, typically located on the underside of the device, to measure the heart’s electrical activity,These devices are capable of detecting atrial fibrillation (AFib).
- While wearable ECGs do not provide the same detailed heart information as a 12-lead ECG, they offer the advantages of on-the-go monitoring and continuous heart health tracking, making heart health data more accessible. However, wearable devices have certain limitations in identifying specific heart conditions.
Why Choose an ECG watch?
- Record ECG at home,Anywhere Anytime.
- One of the main benefits of wearable ECG devices for AFib patients is that they allow users to capture their heart rhythm when symptoms occur, providing valuable information that can be shared with doctors to help manage their health.
- It is important to record symptoms immediately.“they know they’ve got a symptom, but no one can ever capture it at the right time, particularly as AFib can ‘come and go’”a doctor said.
- Continuous heart rate and other health index tracking
What are the right ecg smart watches?
We recommend relevant smart watches that we have collected and tested for you to choose from.
Health Hazards Of AF
Increased Risk of Stroke
AFib can cause blood to pool in the heart, leading to the formation of clots. If a clot travels to the brain, it can block blood flow and cause a stroke. People with AFib are up to five times more likely to experience a stroke than those without it.
Heart Failure
The irregular and often rapid heart rate associated with AFib can weaken the heart over time, making it less efficient at pumping blood and potentially leading to heart failure.
Fatigue and Reduced Quality of Life
The irregular rhythm can cause symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath, which can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Other Complications
Long-term AFib increases the risk of other cardiovascular issues, such as cardiomyopathy, and may worsen existing conditions like hypertension or diabetes.
Best Sellers
Coxsmart Smartwatch with ecg watch Blood Oxygen Heart Rate Health Monitoring
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Use this text to share information about your brand with your customers. Describe a product, share announcements, or welcome customers to your store.